An introduction to extensive reading for Chinese learners
Extensive reading is a powerful tool for Chinese learners aiming to improve their English proficiency. By engaging with large amounts of accessible and enjoyable material, learners can naturally expand their vocabulary, enhance comprehension, and develop fluency. Unlike intensive reading, which focuses on detailed analysis, extensive reading encourages a relaxed approach, allowing learners to absorb language patterns effortlessly. For Chinese students, this method bridges the gap between classroom learning and real-world usage, fostering confidence in reading and communication. Whether through graded readers, novels, or articles, extensive reading offers a practical and enjoyable way to reinforce language skills. This article explores its benefits and provides practical tips for effective implementation.
- An Introduction to Extensive Reading for Chinese Learners
- How do you teach extensive reading?
- What is the most commonly used method for beginning language learners to read Chinese?
- How to study for Chinese reading comprehension?
- How does extensive reading contribute to language and literacy development?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is extensive reading and why is it important for Chinese learners?
- How can Chinese learners choose the right materials for extensive reading?
- What are the key benefits of extensive reading compared to intensive reading?
- How often should Chinese learners practice extensive reading to see progress?
An Introduction to Extensive Reading for Chinese Learners
What Is Extensive Reading?
Extensive reading is a language learning approach where learners read large quantities of material at or slightly below their current proficiency level. Unlike intensive reading, which focuses on detailed analysis, extensive reading emphasizes fluency and enjoyment. For Chinese learners, this method helps improve vocabulary retention, reading speed, and comprehension naturally.
| Key Aspect | Benefit for Chinese Learners |
|---|---|
| Large volume | Builds familiarity with common words and structures |
| Comprehensible input | Encourages understanding without translation |
Why Is Extensive Reading Important for Chinese Learners?
Chinese learners often struggle with character recognition and grammar patterns due to the logographic nature of their native language. Extensive reading provides contextual exposure, helping them internalize sentence structures and idiomatic expressions. Additionally, it reduces reliance on rote memorization by reinforcing words through repetition in context.
See AlsoBest 10 Free Chinese Reading Materials for Beginners to Learn to Read Mandarin| Challenge | How Extensive Reading Helps |
|---|---|
| Character overload | Improves recognition through repeated exposure |
| Grammar complexity | Demonstrates natural usage in sentences |
How to Choose the Right Materials for Extensive Reading
Selecting appropriate texts is crucial. Chinese learners should aim for materials where they understand 90-95% of the content without a dictionary. Options include graded readers, simplified news articles, or children's books. Avoid overly complex texts to maintain motivation and progress.
| Material Type | Suitability |
|---|---|
| Graded readers | Tailored to proficiency levels |
| Bilingual books | Helpful for beginners |
Effective Strategies for Extensive Reading
To maximize benefits, Chinese learners should set daily goals, avoid over-reliance on dictionaries, and track progress. Techniques like skimming and highlighting unknown words (without immediate translation) promote fluency over perfection. Consistency is key—15-30 minutes daily yields better results than sporadic sessions.
| Strategy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Regular practice | Strengthens long-term retention |
| Contextual guessing | Enhances inferencing skills |
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Extensive Reading
Chinese learners often pick overly difficult texts, translate every word, or neglect consistency. These habits hinder progress by causing frustration and slow comprehension. Instead, focus on enjoyable content and gradual difficulty increases to sustain engagement.
See AlsoThe 10 best free Chinese listening resources for beginner, intermediate and advanced learners| Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Overusing dictionaries | Limit look-ups to 1-2 per page |
| Ignoring repetition | Re-read favorite passages |
How do you teach extensive reading?

What is Extensive Reading?
Extensive reading is an approach to language learning where learners read large quantities of material in the target language, focusing on overall comprehension rather than analyzing every word. The goal is to build fluency, vocabulary, and a natural understanding of the language through repeated exposure. Key principles include:
- Reading for pleasure: Learners choose texts that interest them to maintain motivation.
- Minimal dictionary use: Encourages guessing meaning from context to improve comprehension skills.
- Varied material: Includes books, articles, or graded readers tailored to the learner's proficiency level.
How to Select Appropriate Materials
Choosing the right materials is critical for successful extensive reading. Texts should be slightly below the learner's current level to ensure comprehension without frustration. Consider the following:
See AlsoLanguage Exchange: How to Find a Partner?- Graded readers: Specially designed books with controlled vocabulary and grammar.
- Interest-based content: Fiction, non-fiction, or magazines that align with the learner's hobbies.
- Length and complexity: Shorter texts for beginners, gradually increasing in difficulty.
Creating a Supportive Reading Environment
A conducive environment helps learners engage in extensive reading effectively. Teachers and institutions can foster this by:
- Providing access: Libraries or digital resources with a wide range of reading materials.
- Setting goals: Encouraging learners to track progress, such as pages or books read per week.
- Reducing pressure: Avoiding tests or grades to keep the experience enjoyable.
Incorporating Extensive Reading into the Curriculum
To integrate extensive reading into lessons, educators should balance it with other language skills. Strategies include:
- Dedicated reading time: Allocating class time for silent reading sessions.
- Follow-up discussions: Informal chats about what learners read to reinforce comprehension.
- Supplementary activities: Summaries or book reports, but without heavy grading.
Assessing Progress in Extensive Reading
While extensive reading focuses on enjoyment, monitoring progress ensures learners benefit. Assessment methods should be non-intrusive, such as:
See AlsoChinese language learning in the twenty-first century: Towards a digital ecosystem? Interview with Julien Leyre- Reading logs: Learners record titles, pages, and personal reflections.
- Comprehension checks: Simple quizzes or oral questions to gauge understanding.
- Self-assessment: Encouraging learners to reflect on their improvement in fluency and vocabulary.
What is the most commonly used method for beginning language learners to read Chinese?
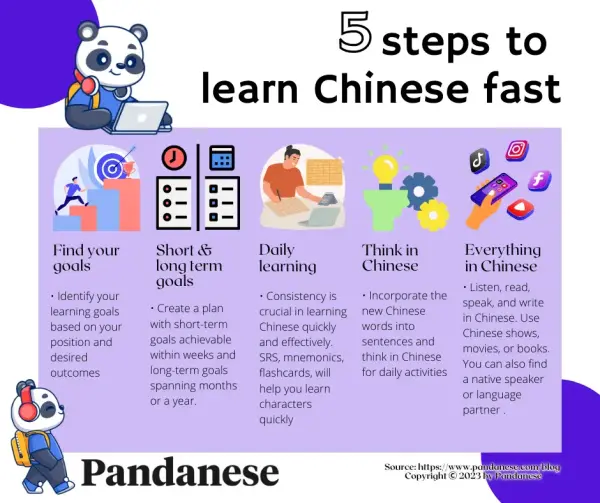
Pinyin as the Foundation for Reading Chinese
The most commonly used method for beginning language learners to read Chinese is Pinyin, a Romanization system that represents Mandarin sounds using the Latin alphabet. Pinyin helps learners associate characters with their pronunciations, making it easier to start reading without immediate mastery of Chinese characters.
- Pinyin breaks down syllables into initials, finals, and tones.
- It serves as a bridge to recognizing and pronouncing characters correctly.
- Many textbooks and apps introduce characters alongside Pinyin for gradual learning.
Learning Basic Characters with Radicals
Another essential method involves studying common radicals (components of Chinese characters) to recognize patterns in written Chinese.
- Radicals often hint at a character’s meaning or pronunciation.
- Learning high-frequency characters first builds a practical vocabulary.
- Tools like flashcards or spaced-repetition apps reinforce character retention.
Graded Readers for Progressive Learning
Graded readers are books tailored for learners at different levels, using simplified language and repetition.
- They introduce vocabulary in context, aiding comprehension.
- Stories often include Pinyin annotations or English translations.
- Progressively increasing difficulty helps learners build confidence.
Using Digital Tools and Apps
Language-learning apps like Duolingo, HelloChinese, and Pleco provide interactive ways to practice reading.
- Apps often combine visual, auditory, and written exercises.
- Features like stroke-order animations teach character writing.
- Spaced repetition systems (SRS) optimize vocabulary retention.
Practicing with Parallel Texts
Parallel texts display Chinese characters alongside translations, helping learners decode meaning.
- They expose learners to natural sentence structures.
- Comparing translations improves contextual understanding.
- Commonly used for short stories, news articles, or dialogues.
How to study for Chinese reading comprehension?

Build a Strong Vocabulary Foundation
To excel in Chinese reading comprehension, you must first develop a robust vocabulary. Start by learning high-frequency words and characters commonly found in texts. Use flashcards or apps like Anki or Pleco to reinforce memorization. Focus on recognizing characters in context rather than isolated memorization.
- Learn radicals to understand character composition and meaning.
- Practice with graded readers tailored to your proficiency level.
- Review vocabulary daily using spaced repetition techniques.
Practice with Authentic Materials
Expose yourself to authentic Chinese texts such as news articles, blogs, or short stories. This helps you adapt to natural language patterns and cultural references. Begin with simpler texts and gradually increase difficulty.
- Read Chinese newspapers like People's Daily or BBC Chinese.
- Follow Chinese social media accounts or forums for informal language.
- Use tools like Pleco’s OCR to look up unfamiliar words instantly.
Master Grammar and Sentence Structure
Understanding Chinese grammar rules is crucial for dissecting complex sentences. Pay attention to word order, particles, and conjunctions. Practice breaking down sentences to identify subjects, verbs, and objects.
- Study common sentence patterns and their variations.
- Analyze parallel structures and conjunctions like 因为...所以.
- Complete grammar exercises from textbooks or online resources.
Develop Skimming and Scanning Techniques
Efficient reading requires skimming for main ideas and scanning for specific details. Train yourself to identify keywords, topic sentences, and summaries quickly.
- Practice timed reading to improve speed and focus.
- Highlight key phrases or recurring themes in passages.
- Summarize paragraphs in your own words to test comprehension.
Take Mock Tests and Review Mistakes
Simulate exam conditions with mock tests to gauge progress. Analyze errors to identify weak areas, such as vocabulary gaps or misinterpretations.
- Use past exam papers or standardized test materials like HSK.
- Keep an error log to track recurring mistakes.
- Review explanations for incorrect answers to avoid repetition.
How does extensive reading contribute to language and literacy development?

How Does Extensive Reading Improve Vocabulary Acquisition?
Extensive reading significantly enhances vocabulary by exposing learners to a wide range of words in context. Unlike intensive reading, which focuses on detailed analysis, extensive reading encourages natural absorption of language patterns. Key benefits include:
- Contextual learning: Readers encounter new words in meaningful sentences, aiding retention.
- Repeated exposure: Frequent encounters with words reinforce memory and understanding.
- Diverse vocabulary: Exposure to different genres introduces varied terminology.
How Does Extensive Reading Enhance Reading Fluency?
Reading fluency improves as learners engage with large volumes of text, reducing hesitation and increasing speed. The process involves:
- Automaticity: Repeated practice helps decode words effortlessly.
- Rhythm and pacing: Natural flow develops through consistent reading habits.
- Reduced cognitive load: Familiarity with common structures allows focus on comprehension.
How Does Extensive Reading Support Grammar and Syntax Understanding?
Grammar and syntax are internalized subconsciously through extensive reading. Learners absorb correct structures without explicit instruction by:
- Pattern recognition: Exposure to well-formed sentences reinforces grammatical rules.
- Natural usage: Readers mimic sentence constructions encountered in texts.
- Error reduction: Frequent exposure minimizes mistakes in writing and speaking.
How Does Extensive Reading Boost Comprehension Skills?
Comprehension skills grow as readers engage with diverse texts, improving their ability to interpret and analyze content. Key aspects include:
- Inference development: Readers deduce meaning from context.
- Critical thinking: Exposure to varied perspectives enhances analytical abilities.
- Text structure familiarity: Recognizing narrative or expository formats aids understanding.
How Does Extensive Reading Foster a Love for Reading?
Motivation and enjoyment are critical outcomes of extensive reading, as learners choose materials aligned with their interests. This leads to:
- Intrinsic motivation: Personal interest drives consistent reading habits.
- Reduced anxiety: Low-pressure environments make reading enjoyable.
- Lifelong learning: Positive experiences encourage continued literacy engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is extensive reading and why is it important for Chinese learners?
Extensive reading is an approach to language learning where learners read large amounts of material that is relatively easy to understand. The goal is to build fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension through repeated exposure to natural language. For Chinese learners, this method is particularly valuable because it helps them internalize sentence structures, idioms, and cultural context in a way that traditional textbook learning often cannot. By focusing on enjoyment and comprehension rather than memorization, learners develop a more intuitive grasp of the language.
How can Chinese learners choose the right materials for extensive reading?
Selecting appropriate materials is crucial for extensive reading to be effective. Chinese learners should look for texts that are slightly below their current proficiency level, allowing them to read smoothly without constant dictionary use. Graded readers, simplified novels, or children's books are excellent starting points. Additionally, learners should prioritize topics of personal interest to maintain motivation. Over time, they can gradually increase the difficulty to include newspapers, blogs, or short stories, ensuring a steady progression in their reading skills.
What are the key benefits of extensive reading compared to intensive reading?
While intensive reading focuses on analyzing short texts in detail, extensive reading emphasizes volume and exposure. For Chinese learners, the benefits include improved reading speed, better retention of vocabulary through context, and increased confidence in tackling longer texts. Extensive reading also fosters a natural understanding of grammar and syntax, as learners absorb patterns subconsciously. Unlike intensive reading, which can feel tedious, extensive reading is often more enjoyable, making it easier to sustain long-term language learning habits.
How often should Chinese learners practice extensive reading to see progress?
Consistency is key for extensive reading to yield results. Chinese learners should aim for daily sessions, even if only for 15-20 minutes, to build a habit and reinforce language acquisition. Over time, increasing the duration to 30-60 minutes per day can accelerate progress. The focus should be on regular exposure rather than cramming, as the brain learns best through repeated, spaced encounters with the language. Tracking the number of books or pages read can also provide motivation and a sense of achievement over time.
Leave a Reply

Related Posts