Interview: Insights from Skritter’s Complete Guide to Learning Chinese
Learning Chinese can be a daunting yet rewarding journey, and having the right tools and strategies is essential for success. In this exclusive interview, we delve into the insights from Skritter’s Complete Guide to Learning Chinese, a comprehensive resource designed to help learners master Mandarin efficiently. From stroke order and character retention to practical study techniques, the guide offers expert advice tailored for both beginners and advanced students. Discover how Skritter’s innovative approach combines technology with proven learning methods to streamline the process. Whether you’re starting from scratch or refining your skills, these insights will provide valuable guidance for your Chinese language journey.
Interview: Key Takeaways from Skritter’s Complete Guide to Learning Chinese
1. The Role of Spaced Repetition in Learning Chinese Characters
Spaced repetition is a core technique emphasized in Skritter’s guide, helping learners retain Chinese characters more effectively. By reviewing characters at optimal intervals, users can strengthen long-term memory. The guide highlights how Skritter’s algorithm adapts to individual progress, ensuring efficient learning.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Adaptive Scheduling | Personalizes review timing based on performance |
| Stroke Order Practice | Reinforces correct character writing habits |
2. Balancing Vocabulary and Grammar in Chinese Studies
Skritter’s approach advocates for a balanced focus on both vocabulary and grammar. The guide suggests integrating high-frequency words early while gradually introducing grammatical structures. This method prevents overwhelm and builds a practical foundation for communication.
See AlsoDuolingo Rewards: Earn XP, Gems, and More| Strategy | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Contextual Learning | Enhances retention through real-life usage |
| Incremental Complexity | Scaffolds learning from simple to advanced |
3. The Importance of Tone Mastery in Mandarin
Mandarin’s tonal nature is a critical challenge for learners. Skritter’s guide stresses consistent tone practice, using audio-visual feedback to train pronunciation. Mispronounced tones can alter meanings, making this skill non-negotiable for fluency.
| Tool | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Interactive Tone Drills | Provides instant correction |
| Minimal Pair Exercises | Sharpens tonal discrimination |
4. Leveraging Technology for Efficient Practice
Skritter’s platform combines technology with proven learning methodologies. Features like handwriting recognition and progress tracking streamline practice sessions. The guide underscores how digital tools can supplement traditional study methods for faster results.
| Technology | Impact |
|---|---|
| Mobile Accessibility | Enables practice anytime, anywhere |
| Data Analytics | Identifies strengths and weaknesses |
5. Cultural Context: Enhancing Language Retention
Understanding cultural nuances deepens language comprehension. Skritter’s guide incorporates cultural notes alongside vocabulary, linking words to traditions or idioms. This holistic approach fosters deeper engagement and recall.
See AlsoLanguages in China (300+ In Total) - A Complete Guide| Element | Value |
|---|---|
| Idiomatic Expressions | Teaches language in cultural context |
| Historical References | Adds layers of meaning to vocabulary |
What do you learn first when learning Chinese?
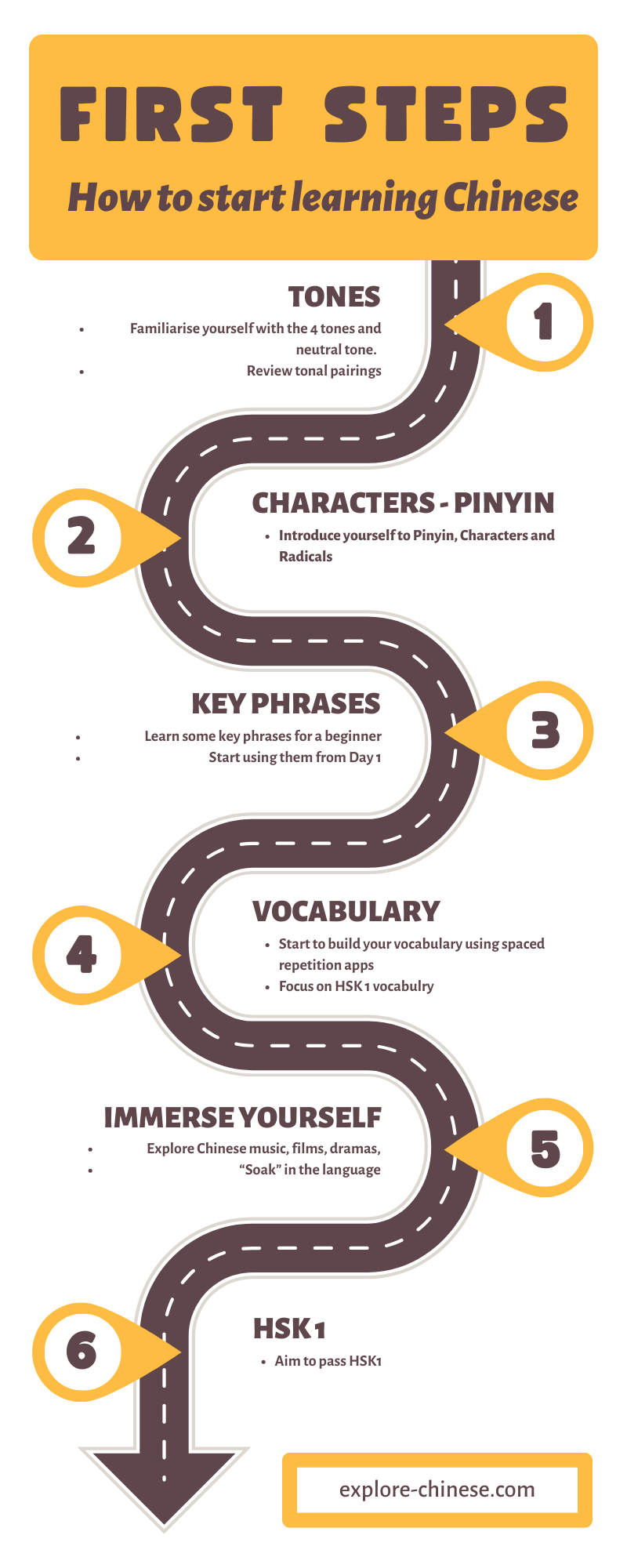
Basic Chinese Pronunciation and Tones
When starting to learn Chinese, mastering pronunciation and tones is crucial. Mandarin has four main tones and a neutral tone, which change the meaning of words entirely. Beginners often focus on:
- Pinyin: The Romanization system to understand sounds.
- Tones: Practicing high, rising, low, and falling tones.
- Common mistakes: Avoiding tone confusion (e.g., mā (mother) vs. mà (scold)).
Essential Chinese Greetings and Phrases
Learning greetings and basic phrases helps build early conversational skills. Key starting points include:
See AlsoHow Appears If You Pass 365 Days On Duolingo: Rewards & Progress- Hello (你好 - nǐ hǎo): The most common greeting.
- Thank you (谢谢 - xiè xiè): A polite essential.
- Goodbye (再见 - zài jiàn): Used in formal and informal settings.
Numbers and Counting in Chinese
Numbers are foundational for daily interactions like shopping or telling time. Beginners typically learn:
- 1-10 (一 to 十): The building blocks for larger numbers.
- Counting systems: Unique structures for tens, hundreds, etc.
- Practical uses: Prices, phone numbers, and dates.
Simple Chinese Characters and Radicals
Early exposure to characters and radicals helps with reading and writing. Focus areas include:
- Basic characters: Like 人 (person) or 日 (sun/day).
- Radicals: Components hinting at meaning or pronunciation.
- Stroke order: Rules for writing characters correctly.
Everyday Vocabulary and Survival Phrases
Practical vocabulary ensures immediate usability. Beginners prioritize:
See AlsoDuolingo Free: Zero-Cost Language Learning Guide [2025 Features]- Food terms: Like 水 (water) or 饭 (rice/meal).
- Directions: Left (左 - zuǒ), right (右 - yòu).
- Emergency phrases: Such as help (帮助 - bāng zhù).
Why is learning Chinese culture important?

Understanding China's Global Influence
Learning Chinese culture is crucial because China plays a significant role in global economics, politics, and technology. By understanding its cultural values, one can better navigate international relations and business opportunities. Key reasons include:
- Economic partnerships: China is a major trade partner for many countries, and cultural awareness fosters smoother negotiations.
- Diplomatic relations: Grasping cultural nuances helps in building stronger political ties.
- Technological advancements: Many innovations originate from China, and cultural insight aids collaboration.
Enhancing Cross-Cultural Communication
Effective communication with Chinese speakers requires more than language proficiency—it demands cultural understanding. Misinterpretations can lead to misunderstandings in both personal and professional settings. Important aspects include:
See AlsoWhat’s your next step to master Chinese?- Non-verbal cues: Gestures and body language hold deep cultural significance.
- Hierarchy and respect: Recognizing the importance of seniority in interactions.
- Indirect communication: Chinese often imply meaning rather than state it directly.
Appreciating Historical and Philosophical Depth
Chinese culture is rooted in millennia of history and philosophy, influencing art, governance, and daily life. Learning about it provides valuable perspectives on human thought and societal development. Key elements are:
- Confucianism: Shapes moral values and social harmony.
- Daoism: Emphasizes balance and natural order.
- Historical dynasties: Offer lessons in leadership and innovation.
Boosting Career Opportunities
Proficiency in Chinese culture can significantly enhance career prospects, especially in multinational companies or roles involving China. Employers value cultural competence for:
- Market expansion: Understanding consumer behavior in China.
- Team collaboration: Working effectively with Chinese colleagues.
- Negotiation skills: Avoiding cultural pitfalls in deals.
Exploring Rich Traditions and Arts
Chinese culture boasts a vibrant heritage of traditions, festivals, and arts, enriching global diversity. Learning about these aspects fosters appreciation and creativity. Highlights include:
- Traditional festivals: Such as Lunar New Year and Mid-Autumn Festival.
- Calligraphy and painting: Reflect deep aesthetic and philosophical values.
- Culinary arts: Regional cuisines with historical significance.
Where to start when learning Chinese?

1. Learn Pinyin and Pronunciation Basics
Mastering Pinyin is the foundation of learning Chinese, as it helps with pronunciation and tones. Chinese is a tonal language, so understanding the four main tones is crucial to avoid misunderstandings.
- Study Pinyin: Learn the Romanization system to pronounce Chinese characters correctly.
- Practice tones: Focus on the four tones (flat, rising, falling-rising, falling) and neutral tone.
- Use audio resources: Listen to native speakers and repeat words to improve accuracy.
2. Build a Basic Vocabulary
Start with high-frequency words and phrases to communicate in everyday situations. Prioritize practical terms over complex vocabulary.
- Learn greetings: Phrases like 你好 (nǐ hǎo) and 谢谢 (xièxie) are essential.
- Numbers and time: Master counting, days of the week, and telling time.
- Common verbs: Focus on action words like 吃 (chī - eat) or 去 (qù - go).
3. Understand Chinese Characters
Chinese characters (Hanzi) are logograms, so learning radicals and stroke order helps in memorization.
- Start with radicals: Recognize common components to decode characters.
- Practice writing: Use grid paper to follow proper stroke order.
- Flashcards: Use apps like Anki or physical cards for repetition.
4. Focus on Grammar and Sentence Structure
Chinese grammar is simpler than many languages, but word order and particles like 了 (le) require attention.
- Subject-Verb-Object (SVO): The basic sentence structure, e.g., 我吃饭 (wǒ chī fàn).
- No conjugations: Verbs don’t change based on tense or person.
- Measure words: Learn classifiers like 个 (gè) for objects.
5. Immerse Yourself in the Language
Exposure to real-life contexts accelerates learning. Use media and practice with native speakers.
- Watch Chinese media: Movies, TV shows, or YouTube channels with subtitles.
- Language exchange: Partner with native speakers via apps like Tandem or HelloTalk.
- Daily practice: Label objects at home or keep a journal in Chinese.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the key insights from Skritter’s Complete Guide to Learning Chinese?
Skritter’s Complete Guide to Learning Chinese offers a wealth of knowledge for learners at all levels. The interview highlights the importance of consistent practice, especially with tools like Skritter that focus on handwriting characters. It emphasizes the value of spaced repetition and active recall to reinforce memory. Additionally, the guide discusses balancing vocabulary acquisition with grammar study to build a solid foundation in Mandarin.
How does Skritter help with mastering Chinese characters?
Skritter is designed to make learning Chinese characters more efficient and engaging. The platform uses adaptive learning algorithms to tailor practice sessions based on individual progress. By focusing on stroke order and character recognition, Skritter helps users develop muscle memory. The interview also notes that its spaced repetition system ensures long-term retention, making it easier to recall characters in real-world contexts.
What strategies does the guide recommend for beginners in Chinese?
For beginners, the guide stresses starting with high-frequency characters and basic grammar structures. It suggests integrating listening and speaking practice early on to develop a natural feel for the language. The interview also recommends using mnemonics to remember characters and avoiding the trap of over-relying on pinyin. Consistency is key, and learners are encouraged to set realistic goals to stay motivated.
Why is handwriting practice important when learning Chinese?
Handwriting practice is crucial because it reinforces character recognition and understanding of radicals. The interview explains that physically writing characters helps embed them in long-term memory more effectively than typing alone. It also improves recall speed and accuracy, which is essential for reading and writing in real-life situations. Skritter’s approach to guided handwriting ensures learners develop proper techniques from the start.
Leave a Reply

Related Posts