Using memory aids and mnemonics to make Chinese easier
Learning Chinese can seem daunting due to its complex characters and tonal system, but memory aids and mnemonics offer powerful tools to simplify the process. By associating characters with vivid images, stories, or familiar concepts, learners can transform abstract symbols into memorable patterns. Mnemonics leverage the brain's natural ability to recall visual and imaginative cues, making retention faster and more enjoyable. Whether through radicals, phonetic components, or creative wordplay, these techniques break down barriers and build confidence. This article explores practical strategies to harness mnemonics effectively, turning the challenge of Chinese into an engaging and achievable journey for learners at any level.
Effective Memory Aids and Mnemonics to Simplify Learning Chinese
Learning Chinese can be challenging due to its complex characters, tones, and grammar. However, using memory aids and mnemonics can significantly ease the process by making abstract concepts more tangible and memorable. These techniques leverage visualization, association, and storytelling to help learners retain vocabulary, characters, and pronunciation more effectively. Below, we explore practical strategies to incorporate these tools into your Chinese learning journey.
1. The Power of Visualization for Chinese Characters
Chinese characters are logographic, meaning each one represents a word or concept. To memorize them, visualization is key. Break characters into smaller components and associate each part with an image. For example, the character 休 (xiū, to rest) combines 亻 (person) and 木 (tree)—imagine a person resting under a tree. This mental picture makes the character easier to recall.
See AlsoPreply Review - Just Another Italki? Or Something Different?| Character | Components | Mnemonic Story |
|---|---|---|
| 好 (hǎo, good) | 女 (woman) + 子 (child) | A woman with a child represents something good. |
| 明 (míng, bright) | 日 (sun) + 月 (moon) | The sun and moon together create brightness. |
2. Using Stories to Remember Vocabulary
Creating short stories around words helps anchor them in your memory. For instance, to remember 飞机 (fēijī, airplane), imagine a flying chicken (fei-ji)—this silly image sticks. The more vivid and absurd the story, the better it works.
| Word | Pinyin | Mnemonic Story |
|---|---|---|
| 牛奶 (niúnǎi, milk) | niú (cow) + nǎi (breast) | A cow’s breast gives milk—think of a cartoon cow. |
| 电话 (diànhuà, phone) | diàn (electric) + huà (talk) | An electric device for talking. |
3. Tonal Mnemonics for Pronunciation
Chinese tones are crucial for meaning. Assign actions or emotions to tones to remember them. For example:
- First tone (high flat): Imagine a robot speaking monotonously.
- Second tone (rising): Pretend you’re asking a question in surprise.
- Third tone (falling-rising): Picture a rollercoaster dip.
- Fourth tone (sharp falling): Think of a stern command.
| Tone | Description | Mnemonic Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | High and flat | Robot voice |
| 2nd | Rising | Question inflection |
4. Radicals as Building Blocks
Radicals are character components that hint at meaning or pronunciation. Learning common radicals (e.g., 氵 for water, 讠 for speech) helps decode new characters. For example, 河 (hé, river) includes 氵, indicating it’s water-related.
See AlsoIs it the Year of the Sheep, Ram or Goat?| Radical | Meaning | Example Character |
|---|---|---|
| 火 (huǒ) | Fire | 炎 (yán, flame) |
| 心 (xīn) | Heart | 想 (xiǎng, to think) |
5. Spaced Repetition with Mnemonics
Combine mnemonics with spaced repetition systems (SRS) like Anki. Review cards with mnemonic hints at increasing intervals to reinforce memory. For example, pair 门 (mén, door) with an image of a menacing door to remember its sound.
| Tool | Mnemonic Integration | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Anki | Add images/stories to flashcards | 猫 (māo, cat) + picture of a meowing cat |
| Pleco | User-created mnemonics | 人 (rén, person) = stick figure |
How can I memorize Chinese words easily?
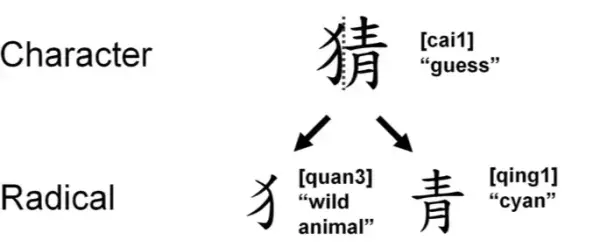
Use Mnemonics to Remember Characters
Mnemonics are memory aids that help you associate Chinese characters with familiar concepts. Break down characters into smaller components and create vivid mental images or stories to link them to their meanings or pronunciations.
See AlsoThe Cthulhu bubble and studying Chinese- Visualize the character's shape as an object (e.g., 木 tree looks like a tree).
- Create stories combining radicals (e.g., 好 good = woman 女 + child 子).
- Use puns or sounds (e.g., 马 mǎ sounds like ma in mama).
Practice Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition systems (SRS) like Anki or Pleco help reinforce memory by reviewing words at optimal intervals. This method ensures long-term retention.
- Schedule reviews based on difficulty (hard words appear more often).
- Mix old and new words to strengthen recall.
- Use flashcards with pinyin, characters, and example sentences.
Write Characters Repeatedly
Writing characters by hand reinforces muscle memory and helps you recognize stroke order and structure.
- Trace characters first to learn stroke order.
- Write without looking to test recall.
- Focus on radicals to understand character composition.
Learn Words in Context
Memorizing isolated words is less effective than learning them in sentences or real-life situations.
- Read short texts like news or stories to see words in action.
- Watch Chinese media (TV shows, movies) with subtitles.
- Practice conversations using new vocabulary.
Associate Words with Sounds or Images
Linking words to sounds, images, or emotions makes them more memorable.
- Use songs or rhymes to remember tones and pronunciation.
- Pair words with pictures (e.g., 猫 cat with a cat image).
- Emotional connections (e.g., 爱 love with a personal memory).
How are mnemonic devices used as memory aids?
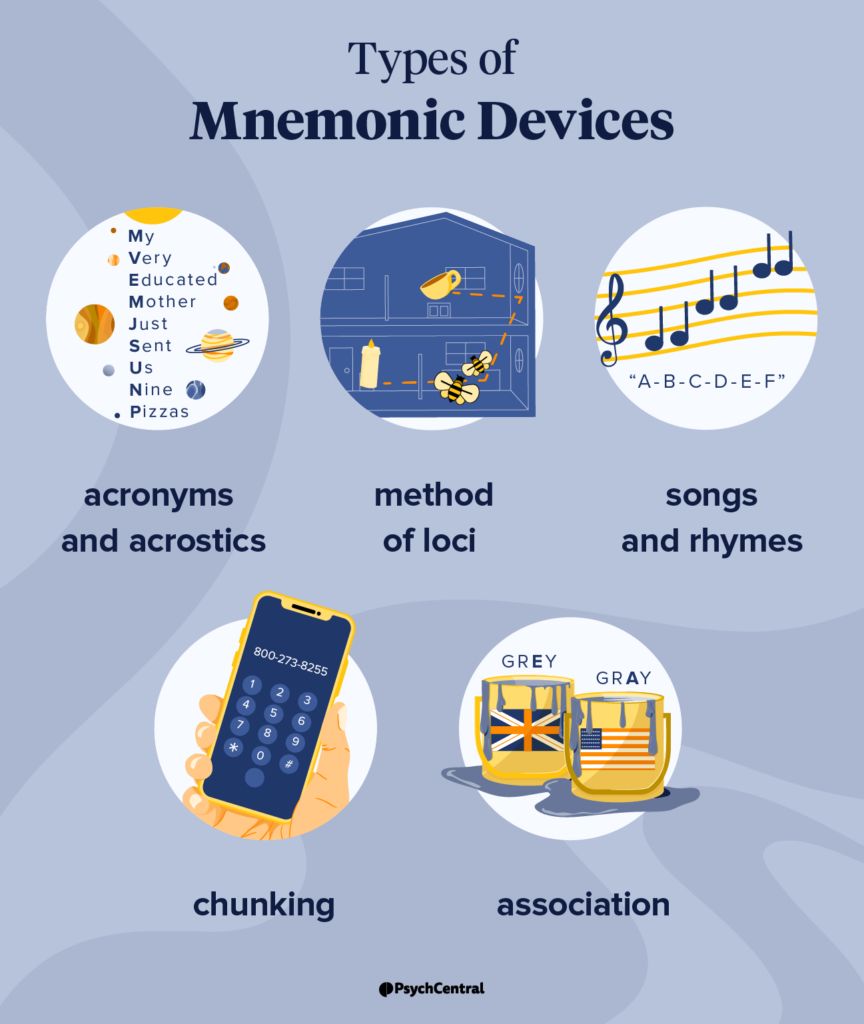
How Do Mnemonic Devices Enhance Memory Retention?
Mnemonic devices improve memory retention by organizing information into patterns or associations that are easier to recall. They simplify complex data by linking it to familiar concepts, such as images, acronyms, or rhymes. For example:
- Acronyms like ROYGBIV help remember the colors of the rainbow (Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet).
- Visualization connects abstract ideas to vivid mental pictures, making them more memorable.
- Rhymes and songs leverage rhythm and melody to embed information in long-term memory.
What Are the Most Common Types of Mnemonic Devices?
Several mnemonic techniques are widely used to aid memory, each suited to different types of information. The most effective include:
- Acronyms and acrostics: Shortening lists into memorable abbreviations (e.g., HOMES for the Great Lakes).
- Chunking: Breaking long sequences (like phone numbers) into smaller, manageable groups.
- Method of loci: Associating items with specific physical locations in a familiar space.
Why Are Mnemonic Devices Effective for Learning?
Mnemonic devices work because they tap into the brain's natural strengths, such as pattern recognition and emotional engagement. Key reasons for their effectiveness:
- Reduced cognitive load: They simplify information, freeing mental resources.
- Dual coding: Combining verbal and visual cues strengthens memory pathways.
- Emotional connection: Humor or novelty in mnemonics makes details stick.
How Can Mnemonic Devices Be Applied in Education?
In educational settings, mnemonics help students master challenging material across subjects. Examples include:
- Science: My Very Educated Mother Just Served Us Noodles for planetary order.
- History: Rhymes to remember dates or events (e.g., In 1492, Columbus sailed the ocean blue).
- Language learning: Associating vocabulary with similar-sounding words in a native language.
What Are the Limitations of Mnemonic Devices?
While powerful, mnemonic strategies have drawbacks depending on context. Key limitations:
- Over-reliance: They may hinder deep understanding if used as a crutch.
- Context-specific: Some mnemonics don’t transfer well to new situations.
- Creation time: Designing effective mnemonics can be time-consuming.
How can I help my child remember Chinese characters?

Use Visual and Story-Based Learning Techniques
Chinese characters are often pictographic or ideographic, making visual associations highly effective. Create stories or images that link the character's shape to its meaning. For example:
- Break down characters into radicals or components and explain their meanings.
- Use mnemonic stories to connect the character's parts to its definition.
- Draw or trace characters while narrating their story to reinforce memory.
Incorporate Repetition and Spaced Practice
Consistent exposure is key to memorizing Chinese characters. Spaced repetition systems (SRS) like flashcards or apps can help:
- Use flashcards with characters on one side and meanings/pronunciations on the other.
- Schedule short, frequent sessions instead of long cramming.
- Review older characters regularly to prevent forgetting.
Make Learning Interactive and Fun
Engage your child with games and activities to make memorization enjoyable:
- Play matching games (characters to meanings or pictures).
- Use tactile methods like writing in sand or with playdough.
- Try digital apps designed for kids, such as Pleco or Skritter.
Connect Characters to Real-Life Contexts
Help your child see practical usage of characters in daily life:
- Label household items with Chinese characters and pinyin.
- Read simple children’s books or comics together.
- Encourage writing short sentences or notes using learned characters.
Leverage Multisensory Learning Approaches
Combine visual, auditory, and kinesthetic methods for deeper retention:
- Say characters aloud while writing them to engage hearing and touch.
- Sing rhymes or songs that include target characters.
- Act out characters with body movements or gestures.
How to memorize a Chinese script fast?

Break Down the Script into Smaller Sections
Memorizing a Chinese script becomes easier when you divide it into manageable parts. Focus on one section at a time, ensuring you understand the meaning and pronunciation before moving forward.
- Segment the script into paragraphs or scenes.
- Analyze the context and emotions behind each section.
- Repeat each segment until you can recite it without errors.
Use Mnemonics and Visual Associations
Linking characters to visual cues or stories helps retention. Mnemonics turn abstract symbols into memorable images.
- Create mental images for complex characters.
- Associate phrases with familiar objects or experiences.
- Use flashcards with pictures to reinforce connections.
Practice Speaking Aloud Repeatedly
Reciting the script out loud strengthens memory retention and improves pronunciation. Repetition is key to fluency.
- Read the script daily with clear articulation.
- Record yourself and compare with native speakers.
- Use shadowing techniques by mimicking audio recordings.
Write the Script by Hand Multiple Times
Writing reinforces muscle memory and helps internalize characters. The physical act of writing improves recall.
- Copy the script slowly, focusing on stroke order.
- Gradually increase speed while maintaining accuracy.
- Test yourself by writing from memory.
Leverage Spaced Repetition Systems (SRS)
Tools like Anki or Pleco optimize memorization by scheduling reviews at increasing intervals.
- Input the script into an SRS app with audio.
- Review cards daily, prioritizing difficult sections.
- Adjust intervals based on your recall rate.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are memory aids and mnemonics, and how can they help with learning Chinese?
Memory aids and mnemonics are techniques designed to improve recall by associating new information with familiar concepts, images, or patterns. In learning Chinese, these tools can simplify the process of memorizing characters, tones, and vocabulary. For example, breaking down a complex character into smaller, recognizable components and creating a story around them can make it easier to remember. Mnemonics leverage the brain's natural ability to retain vivid or unusual associations, turning abstract symbols into meaningful, memorable content.
How do I create effective mnemonics for Chinese characters?
To create effective mnemonics, start by analyzing the structure of a Chinese character and identifying its radicals or components. Then, associate these parts with familiar objects, sounds, or concepts. For instance, the character 好 (hǎo, meaning good) combines 女 (woman) and 子 (child). A mnemonic could be: A woman with a child is a good thing. The more personal, exaggerated, or humorous the association, the stronger the memory retention. Consistency and practice are key—revisiting and refining mnemonics over time reinforces learning.
Can mnemonics help with remembering Chinese tones?
Absolutely! Since tones are crucial in Chinese, mnemonics can link sounds to visual or auditory cues. For example, the first tone (high and flat) might be associated with a musical note held steadily, while the third tone (dipping) could be imagined as a valley in a landscape. Some learners use hand gestures or body movements to physically represent tones, reinforcing muscle memory. Combining these techniques with spaced repetition ensures long-term retention of tonal distinctions.
Are there any downsides to relying on mnemonics for learning Chinese?
While mnemonics are powerful, over-reliance on them can slow down fluency if not paired with active usage. They work best as a scaffolding tool for beginners but should eventually give way to natural recognition through reading, writing, and conversation. Additionally, poorly designed mnemonics may create confusion if associations are too vague or unrelated. Balancing mnemonic techniques with immersive practice—such as listening to native speakers or writing sentences—ensures a well-rounded approach to mastering Chinese.
Leave a Reply

Related Posts