Using Audacity to learn Chinese (speaking and listening)
Learning Chinese, with its unique tones and pronunciation, can be challenging for non-native speakers. However, leveraging free tools like Audacity—a powerful audio editing software—can significantly enhance speaking and listening skills. By recording, slowing down, and analyzing native speech, learners gain better control over tones and fluency. Audacity also allows for repetitive listening, voice comparison, and targeted practice of difficult sounds. Whether mimicking dialogues or dissecting pronunciation, this accessible tool turns passive learning into active engagement. For self-taught students or those supplementing formal lessons, Audacity offers a practical, cost-effective way to refine Mandarin skills and build confidence in real-world conversations.
Using Audacity to Improve Your Chinese Speaking and Listening Skills
Audacity is a powerful, free, and open-source audio editing tool that can significantly enhance your Chinese language learning journey, particularly in speaking and listening. By leveraging its features, learners can record, edit, and analyze their pronunciation, compare it with native speakers, and create customized listening exercises. Below, we explore how Audacity can be optimized for mastering Mandarin Chinese.
1. Recording and Analyzing Your Pronunciation
One of the most effective ways to improve speaking skills is by recording yourself and comparing your pronunciation with native speakers. In Audacity:
- Record your voice while reading Chinese texts or repeating phrases.
- Use the spectrogram or waveform view to visualize pitch and tone patterns.
- Compare your recordings with native audio clips to identify discrepancies.
| Feature | Benefit for Chinese Learning |
|---|---|
| Recording | Practice speaking and self-assess tone accuracy. |
| Spectrogram | Visualize pitch contours to master Mandarin tones. |
2. Creating Custom Listening Exercises
Audacity allows you to edit audio files to create targeted listening drills:
- Slow down speech without altering pitch to better grasp fast dialogue.
- Cut and loop challenging phrases for repeated listening.
- Remove background noise to focus on clear pronunciation.
| Tool | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Change Tempo | Adjust audio speed for comprehension practice. |
| Noise Reduction | Enhance clarity of authentic Chinese audio. |
3. Practicing Tone Recognition with Audacity
Mandarin’s four tones are crucial for meaning. Use Audacity to:
- Isolate tones from native recordings.
- Label tracks to visualize tone shifts (e.g., 妈 mā vs. 马 mǎ).
- Generate tone drills by splicing and rearranging syllables.
| Method | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Tone Isolation | Focus on mastering individual tones. |
| Track Labeling | Map tone contours for visual reinforcement. |
4. Enhancing Listening Comprehension with Looped Playback
Looping difficult sections of dialogues or news clips helps:
- Memorize common phrases and intonation patterns.
- Decipher rapid speech in movies or podcasts.
- Identify key vocabulary in context.
| Technique | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Loop Selection | Reinforce understanding of complex sentences. |
| Bookmarks | Mark key segments for quick review. |
5. Integrating Audacity with Other Learning Resources
Combine Audacity with:
- Anki (create audio flashcards).
- YouTube (extract audio from Chinese lessons).
- Language apps (import dialogues for deeper analysis).
| Resource | Audacity Integration |
|---|---|
| Anki | Embed self-recorded pronunciation checks. |
| YouTube | Convert videos to MP3 for listening drills. |
Can you learn Chinese just by listening?

The Role of Listening in Learning Chinese
Listening is a fundamental part of language acquisition, especially for tonal languages like Chinese. While it helps with pronunciation and auditory recognition, relying solely on listening has limitations. Here’s why:
See AlsoHow to learn Chinese pronunciation as a beginner- Tones: Mandarin Chinese has four distinct tones, and mispronouncing them can change word meanings. Listening helps but requires practice.
- Vocabulary: Passive listening exposes you to words, but active recall and usage are needed for retention.
- Grammar: Chinese sentence structure differs from English. Listening alone may not clarify rules without context.
Can You Achieve Fluency Only by Listening?
Achieving fluency in Chinese through listening alone is unlikely. While it builds comprehension, other skills are essential:
- Speaking: Fluency requires practicing dialogue, not just understanding it.
- Reading/Writing: Chinese characters are logograms, not phonetic, so visual learning is crucial.
- Cultural Context: Idioms and slang often require explanations beyond audio input.
Benefits of Learning Chinese Through Listening
Despite its limitations, listening offers significant advantages when learning Chinese:
- Pronunciation: Mimicking native speakers improves tone accuracy.
- Listening Comprehension: Regular exposure trains the ear for faster understanding.
- Passive Learning: Background listening can reinforce vocabulary subconsciously.
Limitations of Learning Chinese Only by Listening
Exclusive reliance on listening has key drawbacks:
See AlsoHow to find more time to practise Chinese listening- No Feedback: Mistakes in tones or grammar go uncorrected.
- Limited Vocabulary: Rarely used words may be overlooked without structured study.
- No Reading/Writing: Inability to read characters restricts literacy and deeper understanding.
How to Effectively Combine Listening with Other Methods
To maximize progress, integrate listening with other learning strategies:
- Active Listening: Pause and repeat phrases to practice speaking.
- Subtitles/Transcripts: Pair audio with text to connect sounds and characters.
- Language Partners: Engage in conversations to apply listening skills in real-time.
How to improve Chinese fluency?
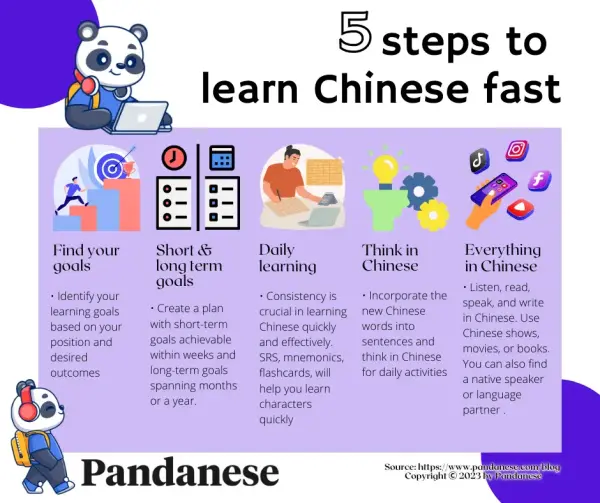
Immerse Yourself in Chinese Daily
To improve fluency, surround yourself with the language as much as possible. This means integrating Chinese into your daily routine in various ways:
- Watch Chinese TV shows or movies with subtitles to train your ear and learn colloquial expressions.
- Listen to Chinese music or podcasts during commutes to familiarize yourself with tones and pronunciation.
- Change your phone or social media settings to Chinese for constant exposure to vocabulary.
Practice Speaking Regularly
Speaking is crucial for fluency. Without active practice, progress will be slow. Here’s how to incorporate it:
- Join language exchange groups or find a native speaker for conversation practice.
- Repeat dialogues aloud from textbooks or videos to improve pronunciation.
- Record yourself speaking and compare it to native speakers to identify areas for improvement.
Expand Vocabulary Strategically
A rich vocabulary is essential for fluency. Focus on learning words that are practical and frequently used:
- Use flashcards or apps like Anki to memorize new words daily.
- Learn words in context by reading articles or books instead of memorizing isolated terms.
- Focus on high-frequency words first, such as those in HSK exam lists, to build a strong foundation.
Master Chinese Characters and Grammar
Understanding characters and grammar is key to forming correct sentences. Here’s how to tackle them:
- Break down characters into radicals to recognize patterns and meanings more easily.
- Practice writing characters by hand to reinforce memory and stroke order.
- Study grammar structures systematically using textbooks or online resources.
Engage with Native Content
Consuming native content helps you understand real-world usage and cultural nuances:
- Read Chinese news or blogs to encounter formal and informal language.
- Follow Chinese influencers or YouTubers to learn slang and modern expressions.
- Participate in forums or comment sections to practice writing and comprehension.
How to revise for Chinese listening?

Understand the Basics of Chinese Pronunciation
To improve your Chinese listening skills, start by mastering the fundamentals of pronunciation and tones. Chinese is a tonal language, meaning the meaning of a word can change based on tone. Focus on these key areas:
- Practice Pinyin: Learn the phonetic system to recognize how words sound.
- Master the four tones: Listen to native speakers and mimic their tone usage.
- Use audio resources: Apps like Pleco or HelloChinese provide pronunciation drills.
Immerse Yourself in Authentic Listening Materials
Exposure to real-life Chinese conversations is crucial for improving comprehension. Use diverse sources to train your ear:
- Watch Chinese TV shows/movies: Start with subtitles, then gradually remove them.
- Listen to podcasts/news: Slow-paced Mandarin podcasts (e.g., ChinesePod) are ideal for beginners.
- Follow native speakers: Engage with YouTubers or social media influencers who speak naturally.
Active Listening and Repetition Techniques
Active listening involves focused engagement with audio materials. Here’s how to maximize retention:
- Shadowing: Repeat sentences immediately after hearing them to improve fluency.
- Transcribe audio clips: Write down what you hear to reinforce recognition.
- Break down dialogues: Analyze unfamiliar words or phrases and review them separately.
Build Vocabulary in Context
Expanding your vocabulary helps you recognize words faster during listening exercises. Focus on practical terms:
- Learn themed vocabulary: Study words related to daily life, travel, or business.
- Use flashcards: Apps like Anki can help memorize high-frequency words.
- Contextual learning: Note how words are used in sentences, not just in isolation.
Simulate Real Exam Conditions (If Preparing for Tests)
For those studying for HSK or other proficiency exams, mimic test conditions to reduce anxiety:
- Take timed practice tests: Use past papers to familiarize yourself with the format.
- Focus on question patterns: Identify common question types (e.g., main idea, details).
- Review mistakes: Analyze errors to avoid repeating them in the actual exam.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How can Audacity help improve my Chinese speaking skills?
Audacity is a powerful tool for improving your Chinese speaking skills because it allows you to record and playback your voice. By recording yourself speaking Chinese, you can compare your pronunciation with native speakers or audio samples. This helps identify areas where you need improvement, such as tones, intonation, or fluency. Additionally, you can use the speed adjustment feature to slow down recordings of native speakers, making it easier to mimic their speech patterns.
What features in Audacity are most useful for learning Chinese listening?
Audacity offers several features that enhance Chinese listening practice. The noise reduction tool helps clean up audio files, making it easier to hear clear pronunciations. The amplification feature allows you to increase the volume of quiet recordings. You can also use the loop playback function to repeatedly listen to difficult phrases or sentences. Another useful tool is the spectrogram view, which visually represents speech patterns, helping you understand the pitch and rhythm of Chinese words.
Can I use Audacity to practice Chinese tones effectively?
Yes, Audacity is excellent for practicing Chinese tones. By recording yourself and comparing your tones to native speakers, you can spot discrepancies in your pronunciation. The pitch track feature visually displays the contour of your voice, allowing you to see if you’re matching the correct tone patterns (e.g., rising for Tone 2 or falling-rising for Tone 3). You can also slow down recordings to hear the subtle differences in tones more clearly, which is crucial for mastering Mandarin’s tonal nature.
How do I import Chinese audio lessons into Audacity for practice?
To import Chinese audio lessons into Audacity, simply go to File > Open and select your audio file (e.g., MP3 or WAV format). Alternatively, you can drag and drop the file directly into the Audacity workspace. Once imported, you can edit the audio by cutting out unnecessary sections, adjusting the speed, or applying effects like equalization to enhance clarity. For online resources, you can use Audacity’s recording feature to capture audio from websites or apps playing Chinese lessons.
Leave a Reply

Related Posts