How to become a Chinese-English translator and what it’s like to be one
Becoming a Chinese-English translator is a rewarding career path that bridges cultures and facilitates global communication. This profession requires not only fluency in both languages but also a deep understanding of cultural nuances, industry-specific terminology, and translation techniques. Whether working in business, legal, literary, or technical fields, translators play a crucial role in making content accessible across linguistic barriers. This article explores the essential steps to enter the field, from honing language skills to gaining professional certifications, while also offering insights into the daily challenges and satisfactions of the job. Discover what it takes to succeed and what to expect in this dynamic and ever-evolving profession.
How to Become a Chinese-English Translator and What It’s Like to Be One
Becoming a Chinese-English translator requires a combination of language proficiency, cultural understanding, and specialized skills. This career path offers diverse opportunities, from freelance work to corporate roles, but it also demands dedication and continuous learning. Below, we explore the key steps to entering this field and the realities of working as a translator.
1. Essential Skills for a Chinese-English Translator
To excel as a Chinese-English translator, you must master both languages at a native or near-native level. This includes grammar, vocabulary, and idiomatic expressions. Additionally, cultural awareness is crucial to accurately convey context and nuance. Translators often specialize in fields like legal, medical, or technical translation, requiring industry-specific knowledge.
See AlsoHow To Read Stories On Duolingo: Improve Reading Practice| Skill | Importance |
|---|---|
| Bilingual Proficiency | High |
| Cultural Competence | Critical |
| Specialized Knowledge | Varies by Field |
2. Education and Certification Requirements
While a degree in translation, linguistics, or a related field is beneficial, it’s not always mandatory. Many translators pursue certifications like the ATA (American Translators Association) certification to validate their skills. Continuous learning through courses and workshops helps stay updated with language trends and industry standards.
| Qualification | Relevance |
|---|---|
| Bachelor’s Degree | Helpful but Not Required |
| ATA Certification | Enhances Credibility |
3. Finding Work as a Chinese-English Translator
Translators can work freelance, in-house, or for agencies. Platforms like ProZ and Upwork offer freelance opportunities, while corporations and government agencies hire in-house translators. Building a strong portfolio and networking are key to securing consistent work.
| Work Type | Pros & Cons |
|---|---|
| Freelance | Flexibility but Unstable Income |
| In-House | Stability but Less Flexibility |
4. Challenges Faced by Chinese-English Translators
Common challenges include tight deadlines, complex terminology, and maintaining accuracy while preserving the original tone. Machine translation tools like Google Translate can assist but often lack nuance, requiring human intervention.
See AlsoShapeshifting Chinese characters| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Deadline Pressure | Time Management |
| Technical Jargon | Specialized Training |
5. The Rewards of Being a Chinese-English Translator
This career offers intellectual stimulation, cultural exchange, and the satisfaction of bridging language barriers. Translators often work on diverse projects, from literature to business contracts, making the role dynamic and engaging.
| Reward | Impact |
|---|---|
| Cultural Exchange | Broadens Perspectives |
| Career Diversity | Multiple Opportunities |
How do I become a certified Chinese English translator?
Understanding the Requirements for Certification
To become a certified Chinese-English translator, you must first understand the specific requirements set by recognized certification bodies. These typically include:
See AlsoThe importance of counting what counts when learning Chinese- Language proficiency: Fluency in both Chinese and English, often verified through standardized tests like HSK for Chinese or IELTS/TOEFL for English.
- Educational background: A degree in translation, linguistics, or a related field is preferred but not always mandatory.
- Experience: Some certifications require proof of professional translation experience, usually 2+ years.
Choosing the Right Certification Program
Selecting the right certification program is crucial for your career. Consider the following:
- Accreditation: Ensure the program is recognized by industry bodies like ATA (American Translators Association) or CIOL (Chartered Institute of Linguists).
- Exam structure: Research whether the test focuses on general translation, specialized fields (legal, medical), or both.
- Cost and location: Compare fees and whether exams are offered online or in-person.
Preparing for the Certification Exam
Effective preparation is key to passing the certification exam. Follow these steps:
- Study materials: Use official guides, past papers, and recommended textbooks.
- Practice translations: Work on diverse texts (e.g., legal, technical) to build versatility.
- Mock exams: Simulate test conditions to improve time management and accuracy.
Gaining Practical Experience
Hands-on experience strengthens your skills and resume. Focus on:
- Freelance projects: Platforms like ProZ or Upwork offer opportunities to work on real translations.
- Internships: Join translation agencies or multinational companies for structured experience.
- Networking: Attend industry events to connect with professionals and learn about job openings.
Maintaining and Advancing Your Certification
After certification, stay competitive by:
- Continuing education: Take advanced courses or workshops to refine specialized skills.
- Renewal requirements: Some certifications require periodic renewal through exams or professional development credits.
- Specialization: Consider niche areas like legal or medical translation to increase demand for your services.
How to be a Chinese translator?

Master the Chinese Language
To become a Chinese translator, you must achieve fluency in both Mandarin and your native language. Focus on:
- Grammar and syntax: Study Chinese sentence structure and compare it to your native language.
- Vocabulary: Build a robust lexicon, including idioms and technical terms.
- Pronunciation: Practice tones and accents to understand regional variations.
Gain Cultural Understanding
Translation goes beyond words; it requires deep cultural knowledge. Key areas include:
- History and traditions: Understand context for accurate translations.
- Social norms: Recognize formal vs. informal language usage.
- Pop culture: Stay updated on trends for modern translations.
Develop Translation Skills
Effective translation demands specialized techniques. Improve by:
- Practicing daily: Translate articles, books, or speeches.
- Using CAT tools: Learn software like Trados or MemoQ.
- Proofreading: Refine drafts for clarity and accuracy.
Obtain Professional Certification
Certifications validate your expertise. Consider:
- HSK exam: Prove Mandarin proficiency (Level 6 for advanced).
- ATA certification: Earn credentials from the American Translators Association.
- Specialized courses: Enroll in legal, medical, or technical translation programs.
Build a Career Network
Success depends on connections and visibility. Strategies include:
- Freelance platforms: Join Upwork or ProZ for gigs.
- Industry events: Attend conferences or webinars.
- Social media: Showcase work on LinkedIn or professional forums.
Do Chinese translators make good money?
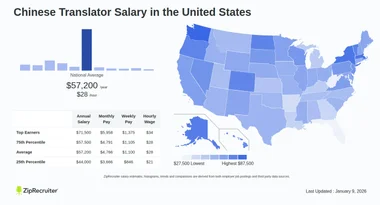
How Much Do Chinese Translators Earn on Average?
The average salary for Chinese translators varies depending on factors like experience, specialization, and location. In China, entry-level translators may earn between $10,000 and $20,000 annually, while experienced professionals can make $30,000 to $60,000 or more. Freelancers often charge per word or project, with rates ranging from $0.05 to $0.20 per word.
- Entry-level translators typically earn less but gain experience quickly.
- Specialized fields (legal, medical, technical) command higher rates.
- Freelancers have fluctuating incomes but more flexibility.
What Factors Influence a Chinese Translator's Salary?
A translator's income depends on several key factors. Language pairs (e.g., Chinese-English) are in high demand, but niche combinations may pay more. Industry demand, such as in tech or finance, also boosts earnings. Additionally, certifications (like CATTI in China) and remote work opportunities can increase pay.
- Demand for language pairs affects market rates.
- Industry specialization leads to higher-paying jobs.
- Certifications validate skills and justify higher fees.
Is Freelance or Full-Time Work More Lucrative for Chinese Translators?
Both freelance and full-time roles have pros and cons. Full-time positions offer stability, benefits, and salaries of $25,000 to $50,000 annually. Freelancers can earn more per project but face inconsistent workloads. Top freelancers with strong client networks may surpass $70,000 per year.
- Full-time jobs provide steady income and benefits.
- Freelancers can set higher rates but manage irregular income.
- Networking is crucial for freelance success.
Which Industries Pay the Highest Salaries for Chinese Translators?
Certain industries offer premium pay for Chinese translation services. Legal and medical translators often earn the most due to complexity and liability. Technical and financial sectors also pay well, with rates exceeding $0.15 per word. Government and diplomatic roles may provide additional perks.
- Legal translation requires precision and pays top rates.
- Medical translators need specialized knowledge.
- Tech and finance sectors value accuracy and speed.
How Does Location Affect a Chinese Translator's Earnings?
Geographical location significantly impacts earnings. Translators in major cities (Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen) or working for international clients earn more. Those in rural areas or smaller markets may see lower rates. Remote work allows access to global clients, potentially increasing income.
- Urban areas offer higher salaries and more opportunities.
- International clients often pay better than local ones.
- Remote work expands earning potential globally.
Are Chinese translators in demand?

Why Are Chinese Translators in High Demand Globally?
The demand for Chinese translators has surged due to China's growing influence in global trade, technology, and diplomacy. Businesses, governments, and organizations require professionals who can bridge the language gap. Key reasons include:
- Economic expansion: China is a major player in international markets, necessitating translation for contracts, negotiations, and marketing.
- Technological advancements: Chinese tech firms like Huawei and Alibaba operate worldwide, requiring localization of products and services.
- Cultural exchange: Increased interest in Chinese media, literature, and education drives demand for skilled translators.
Which Industries Need Chinese Translators the Most?
Several industries heavily rely on Chinese translators to facilitate communication and operations. The top sectors include:
- E-commerce: Platforms like Amazon and eBay need translations for product listings targeting Chinese consumers.
- Legal and finance: Cross-border transactions and compliance documents require precise translation.
- Healthcare: Medical research and pharmaceutical collaborations between China and other countries depend on accurate translations.
What Skills Are Essential for Chinese Translators?
To succeed as a Chinese translator, professionals must possess a combination of linguistic and technical skills. Critical competencies include:
- Bilingual proficiency: Mastery of both Mandarin and the target language is non-negotiable.
- Cultural awareness: Understanding nuances and idioms ensures accurate and context-appropriate translations.
- Technical expertise: Familiarity with translation tools like CAT software improves efficiency and consistency.
How Does Freelancing Compare to Full-Time Roles for Chinese Translators?
Both freelancing and full-time positions offer opportunities for Chinese translators, but they differ in flexibility and stability. Key contrasts include:
- Income variability: Freelancers may earn more per project but lack steady paychecks, while full-time roles provide fixed salaries.
- Workload control: Freelancers choose projects, whereas full-time translators often follow employer assignments.
- Benefits: Full-time positions typically include health insurance and retirement plans, which freelancers must secure independently.
What Are the Future Trends for Chinese Translators?
The future of Chinese translation is shaped by technological and geopolitical developments. Emerging trends include:
- AI integration: Machine translation tools assist but cannot replace human translators for nuanced tasks.
- Specialization: Demand grows for translators with expertise in niche fields like AI, law, or medicine.
- Remote work: Globalization enables translators to work for clients worldwide without geographical constraints.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What qualifications do I need to become a Chinese-English translator?
To become a Chinese-English translator, you typically need a strong command of both languages, including fluency in Mandarin Chinese and English. Many employers or clients prefer candidates with a bachelor’s degree in translation, linguistics, or a related field. Additionally, obtaining a professional certification, such as the American Translators Association (ATA) certification or a Chinese government-approved translation license, can significantly enhance your credibility. Specialized knowledge in industries like legal, medical, or technical translation may also be required depending on the job.
How can I gain experience as a Chinese-English translator?
Gaining experience as a Chinese-English translator often starts with internships, freelance projects, or volunteer work for non-profits. Platforms like ProZ, Upwork, or TranslatorsCafé can help you find entry-level opportunities. Building a portfolio with diverse samples of your work is crucial. Networking with professionals in the field, joining translation associations, and attending industry conferences can also open doors to more advanced roles. Over time, you may specialize in a niche to increase your marketability.
What are the daily responsibilities of a Chinese-English translator?
A Chinese-English translator typically handles tasks such as translating documents, proofreading, and localizing content to ensure cultural appropriateness. Daily work may involve collaborating with clients or agencies, meeting tight deadlines, and using CAT tools (Computer-Assisted Translation) like Trados or MemoQ for efficiency. Translators often research industry-specific terminology and stay updated on language trends. Freelancers may also spend time marketing their services and managing administrative tasks like invoicing.
What are the challenges of being a Chinese-English translator?
One of the biggest challenges is maintaining linguistic accuracy while ensuring the translation sounds natural in the target language. Cultural nuances and idiomatic expressions can be particularly tricky. Additionally, working under tight deadlines or dealing with highly specialized content (e.g., legal or medical texts) can be stressful. Freelancers may face irregular income and competition from low-cost providers. However, overcoming these challenges can lead to a rewarding career with opportunities for growth and specialization.
Leave a Reply

Related Posts